ON THIS PAGE
Apr 12, 2020 The general rule when configuring DHCP snooping is to “trust the port and enable DHCP snooping by VLAN”. Therefore, the following steps should be used to enable or configure DHCP snooping: Step 1. Enable DHCP snooping using the ip dhcp snooping global configuration command. On trusted ports, use the ip dhcp snooping trust interface.
DHCP local server receives DHCP request andreply packets from DHCP clients and then responds with an IP addressand other optional configuration information to the client.
Configuring Address Pools for DHCP Dynamic Bindings
For dynamic bindings, set aside a pool of IP addressesthat can be assigned to clients. Addresses in a pool must be availableto clients on the same subnet.
To configure an address pool, include the followingstatements at the address-range statement definesthe lowest and highest IP addresses in the pool that are availablefor dynamic address assignment. This statement is optional. If norange is specified, the pool will use all available addresses withinthe subnet specified. (Broadcast addresses, interface addresses, andexcluded addresses are not available.)
The DHCPDISCOVER packet is received. When more than one pool exists on the same interface,addresses are assigned on a rotating basis from all available pools.
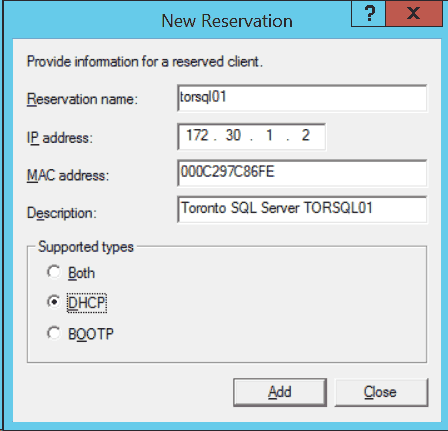
Configuring Manual (Static) DHCP Bindings Between a Fixed IPAddress and a Client MAC Address
Static bindings provide configuration informationfor specific clients. This information can include one or more fixedInternet addresses, the client hostname, and a client identifier.
To configure static bindings, include the followingstatements at the mac-address variable specifies the MAC address of the client. This is a hardwareaddress that uniquely identifies each client on the network.
The host statement specifies the hostnameof the client requesting the DHCP server. The name can include thelocal domain name. Otherwise, the name is resolved based on the client-identifier statement is used by the DHCP server to indexthe database of address bindings. The client identifier is eitheran ASCII string or hexadecimal digits. It can include a type-valuepair as specified in RFC 1700, Assigned Numbers. Either a client identifier or the client’s MAC address mustbe configured to uniquely identify the client on the network.
NoteFor each unique client-id value, the DHCP server issues a uniquelease and IP address from the pool. Previously, when the client providedan incorrect client-id value, the DHCP server did not issue a lease.
The following is an example of a static bindingconfiguration:
Specifying DHCP Lease Times for IP Address Assignments
For clients that do not request a specific leasetime, the default lease time is one day. You can configure a maximumlease time for IP address assignments or change the default leasetime.
To configure lease times, include the default-lease-time statements:
Borderlands 2 shift codes ps4. You can get thebest discountof upto 95% off.The new discount codes are constantly updated on Couponxoo. This is easily done with searching onCouponxoo’sBox. The latest onesare onMay 15, 202012 newBorderlands 2 Community Day Shift Codes results have been found in the last 90days, whichmeans that every 8, a newBorderlands 2 Community Day Shift Codes result is figured out.As Couponxoo’s tracking, online shoppers can recently get a save of50% on average by using our couponsfor shoppingatBorderlands 2 Community Day Shift Codes. Borderlands 2 Community Day Shift Codes OverviewBorderlands 2 Community Day Shift Codes can offer you many choices to savemoney thanks to23 active results.
You can include these statements at the followinghierarchy levels:
Lease times defined for static bindings and addresspools take priority over lease times defined at the maximum-lease-time statement configuresthe maximum length of time in seconds for which a client can requestand hold a lease. If a client requests a lease longer than the maximumspecified, the lease is granted only for the maximum time configuredon the server. After a lease expires, the client must request a new lease.
NoteMaximum lease times do not apply to dynamicBOOTP leases. These leases are not specified by the client andcan exceed the maximum lease time configured.
The following example shows a configuration formaximum and default lease times:
Configuring a DHCP Boot File and DHCP Boot Server
When a DHCP client starts, it contacts a boot serverto download the boot file.
To configure a boot file and boot server, includethe boot-server statements:
You can include these statements at the followinghierarchy levels:
After a client receives a DHCPOFFER response from a DHCP server, the client can communicate directlywith the boot server (instead of the DHCP server) to download theboot file. This minimizes network traffic and enables you to specifyseparate boot server/file pairs for each client pool or subnetwork.
The boot-server statement configuresthe IP address of the TFTP server that contains the client’sinitial boot file. You must configure an IP address or a hostnamefor the server.
You must configure at least one boot file and bootserver. Optionally, you can configure multiple boot files and bootservers. For example, you might configure two separate boot serversand files: one for static binding and one for address pools. Bootfile configurations for pools or static bindings take precedence overboot file configurations at the server-identifier statement:
You can include this statement at the followinghierarchy levels:
The domain-name statement:
You can include this statement at the followinghierarchy levels:
The domain-search statement:
You can include this statement at the followinghierarchy levels:
The domain-search statement is optional,if you do not configure a domain search list, the default is the client’scurrent domain.
Configuring Routers Available to the DHCP Client
After a DHCP client loads the boot image and hasbooted, the client sends packets to a router.
To configure routers available to the DHCP client,include the router statement specifies a listof IP addresses for routers on the client’s subnet. List routersin order of preference. You must configure at least one router foreach client subnet.
The following example shows routers configuredat the option statement:
The id-number—Anywhole number. The ID number is used to index the option and must beunique across a DHCP server.
byte
option-value—Value associated with an option. The option value must becompatible with the option type (for example, an Off value for a option3 router statement and uses the [edit interfaces] hierarchy level. The interface’s primaryaddress (
10.3.3.1/24) has a correspondingaddress pool (10.3.3.0/24) definedat the [edit system services] hierarchy level include the following:Verifying and Managing the DHCP Server Configuration
To display the client address bindings for the extended DHCPlocal server, use the following operational commands:
show dhcp server statistics
To clear client address bindings and DHCP local server statistics,use the following operational commands:
clear dhcp server statistics
For information about using these operations commands, see the show system services dhcpbinding
The following example shows the binding type andlease expiration times for IP addresses configured on a router thatsupports a DHCP server:
Enter an IP address to show binding for a specificIP address:
user@host> detail option to show detailedbinding information:user@host> show system services dhcp pool command to view information about DHCP address pools.The following example show address pools configuredon a DHCP server:
Example: Viewing and Clearing DHCP Conflicts
When the DHCP server provides an IP address, theclient performs an ARP check to make sure the address is not beingused by another client and reports any conflicts back to the server.The server keeps track of addresses with conflicts and removes themfrom the address pool. Use the CLI command clear system services dhcp conflicts command to clear the conflicts list and return IP addresses to thepool. The following command shows how to clear an address on the serverthat has a conflict:
user@host> traceoptions statement at the [edit systemservices dhcp traceoptions] hierarchy level:Tasks for configuringDHCP tracing operations are:
Configuring the DHCP Processes Log Filename
By default, the name of the file that records traceoutput is dhcpd. You can specifya different name by including the file statement at the filename.0, then (filename.2) is overwritten.
You can configure the limits on the number andsize of trace files by including the following statements at the filename
) reaches 2 MB, filename.0, and a new file called filename reaches 2 MB, filename.1 and filename.0. This process repeatsuntil there are 20 trace files. Then the oldest file (filename.0).The number of files can be from 2 through 1000files. The file size of each file can be from 10KB through 1 gigabyte(GB).
Configuring Access to the DHCP Log File
By default, log files can be accessed only by theuser who configures the tracing operation.
To specify that any user can read all log files,include the [editsystem services dhcp traceoptions] hierarchy level:
To set the default behavior explicitly, includethe [editsystem services dhcp traceoptions] hierarchy level:
HDD Password Tool is a small utility by Toshiba which allows you to lock and unlock data access on disk drives, storage medium and USB thumb drives. In order to protect yourself and your data from unauthorized access, Toshiba has created this nifty utility to add a password to your data. Hdd pw.exe dos. Installing the HDD Password Protection download: Exlade provides their software as a Windows Executable file and therefore installation is as easy as downloading the file diskppsetup.exe and running it directly after retrieving it. We highly suggest using antivirus software before running.any. files from the Internet. The company hosting this file has a trust rating of 5/10. Hddpw.exe - Google Drive. BIOSPW.EXE BIOS Password Removal Utility. This is the companion to hddpw.exe from above. Other people have already described it, so best see there for an explanation. Biospw.exe (17 kB) biospw.exe.gz (compressed; 10 kB). I’m Using 64bit Windows—What Now? The 64-bit versions of Windows can’t run DOS programs anymore, at least not directly.
Configuring a Regular Expression for Refining the Output ofDHCP Logged Events
By default, the trace operations output includesall lines relevant to the logged events.
You can refine the output by including the matchstatement at the filename] hierarchy level and specifying a regularexpression (regex) to be matched:
Configuring DHCP Trace Operation Events
By default, only important events are logged. Youcan configure the trace operations to be logged by including the followingoptions at the
Flag
Operation or Event
All operations.
Binding operations.
Logins to the configuration database.
Client-detected conflicts for IP addresses.
Important events.
Interface database operations.
I/O operations.
Lease operations.
Main loop operations.
Miscellaneous operations.
DHCP packets.
DHCP options.
Address pool operations.
Protocol operations.
Routing socket operations.
Scope operations.
DHCP signal operations.
Tracing operations.
User interface operations.
Related Documentation